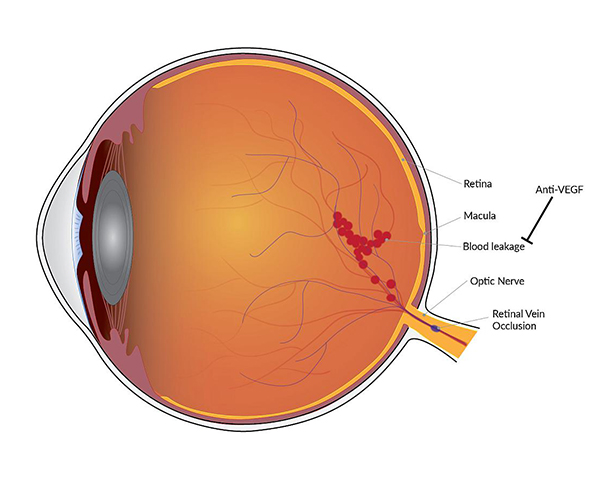
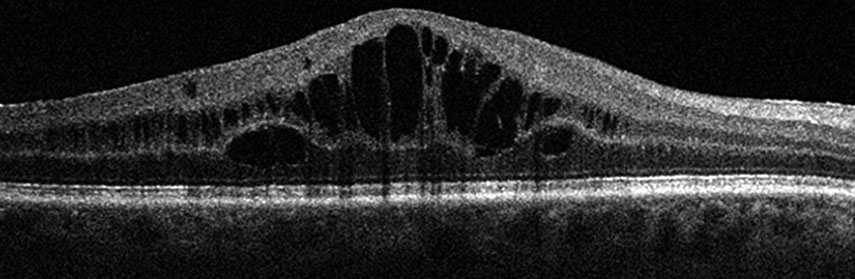
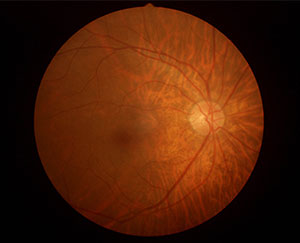
Retinal Vein Occlusion(RVO)
Retinal Vein Occlusion is a condition in which one or more veins that carry blood away from the retina become blocked or obstructed. This results in the reduced flow of blood to the affected region of the retina. RVO can lead to a number of conditions, including blurry vision, dark spots or floaters, and, in severe cases, complete loss of vision. Individuals at a higher risk of developing RVO include those with a history of diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, and heart disease. Smoking and a sedentary lifestyle can also increase the risk of developing RVO.
Untreated RVO can cause serious complications, leading to permanent vision loss and blindness. If you experience sudden disturbances in your vision in any one of the eyes, you should seek medical advice promptly.
Symptoms may include
- Blurred or distorted vision
- Partial/ complete loss of vision
- Sudden onset of floaters
- Visual field loss
- A dark or empty spot in your vision
These symptoms might indicate a retinal vein occlusion (RVO). These conditions can cause permanent vision loss or other complications if not treated promptly.