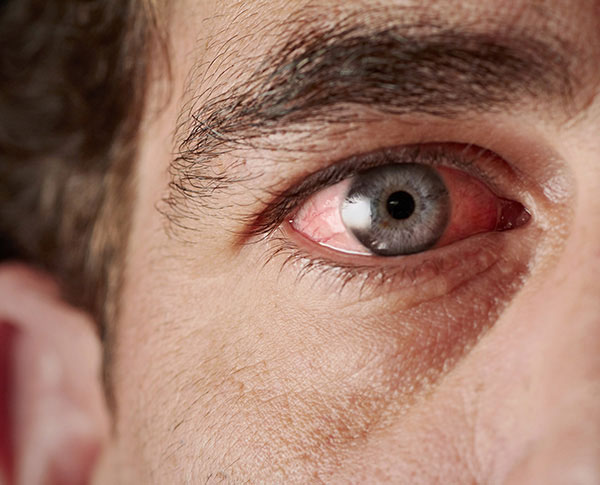
Red eyes can be caused by Dry eyes
Small glands located above the eyes produce tears. They function to lubricate and protect the eyes. When your eyes don't produce enough tears, you have dry eyes.
Studies have shown that dry eyes frequently occur, with prevalence rates ranging from 5 to 50%. Women, those over the age of 50, and people who wear contact lenses have a higher risk of developing the illness and red eyes.
If you have dry eyes, you can observe eye redness and pain. Other signs comprise:
- a stinging, itchy, or burning sensation
- a feeling as something is in your eyes
- light sensitivity and
- blurred vision (that comes and goes, especially when reading)
Conjunctivitis can be one reason for Red eyes
The membrane lining the inside of your eyelids and the white area of your eye, known as the conjunctiva, can become inflamed and cause conjunctivitis. Pink eye/red eyes is another name for this ailment. The pink or red tint of your eyes' whites results from conjunctival inflammation.
Conjunctivitis may also cause the following additional symptoms:
- Itching
- Burning sensation
- Tearing becomes more frequent
- When there is an obstruction in the eye and mucus or pus is discharged; this can cause crusting of the eyelids or eyelashes
There are numerous possible causes of conjunctivitis, such as:
- Bacterial infections that can be brought on by Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, or Haemophilus influenzae
- Viral infections, such as those brought on by Adenoviruses, Measles, or COVID-19
- Allergies to things like pollen, moulds, and pet dander
- Environmental irritants like smoke or chemical fumes
Viral or bacterial conjunctivitis spreads quickly and is highly contagious. It can therefore be quickly transferred from one person to another.
Blepharitis can cause Red Eyes
Inflammation of the eyelids is referred to as blepharitis. Your eyelids or eyes could look red and puffy as a result, and you can have what is also called bloodshot eyes.
Additional signs of blepharitis include the following:
- increased tearing,
- a burning or stinging sensation,
- feeling like something is in your eye, causing your eyes to be red and painful,
- itching,
- crusty eyelids in the morning, and
- sensitivity to light, are some of the symptoms
Blepharitis may potentially result in more severe red eye symptoms, especially if it is not treated. These may include eyesight blurriness, eyelash growth in the incorrect place, eyelash loss, eye pain, and redness.
If you have a lot of bacteria on your eyelids, blepharitis may develop. The illness may also worsen if the oil glands in your eyelids clog up. A mite infestation can occasionally bring on blepharitis.
Uveitis can be one reason for Red eyes
Inflammation, or uveitis, affects the uvea, the central region of your eye. The uvea is the region between the retina and the white of your eye.
Eye redness/ red eyes may be caused by uveitis-related inflammation. Additional signs to watch for are:
- blurry vision
- eye discomfort
- floaters
- sensitivity to light
Uveitis can be brought on by several factors, including:
- certain forms of infections, such as syphilis, shingles, and toxoplasmosis
- some cancers, such as lymphoma;
- the herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 1
- autoimmune illnesses like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and ulcerative colitis
Uveitis must be treated as soon as possible. This is because if the illness is not controlled, it can lead to red eyes, which may cause vision loss.
Scleritis can be a reason for Red eyes
When the sclera, the white of your eye, becomes inflamed, it is known as scleritis. The white of your eye may turn red and puffy or bloodshot eyes when this happens. Other signs and symptoms include:
- Hazy vision
- More sensitivity to light
- Head, facial, or jaw pain
- Increased crying
- Tenderness or pain in the eyes
- Lowered vision
Scleritis frequently occurs alongside an autoimmune disorder. Some instances are:
- Sjögren's syndrome
- Lupus
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- An inflammatory bowel illness, Crohn's disease, or ulcerative colitis
Additionally, scleritis may develop due to an eye infection or damage due to red eyes.
Subconjunctival haemorrhage can cause Red Eyes
Blood can occasionally seep from a broken blood artery in your bloodshot eye, covering the surface of your eye. A subconjunctival haemorrhage is what this is.
Although the disease may appear dangerous, it is frequently benign and resolves naturally in 1 to 2 weeks. Usually, the only symptom of red eyes is the redness of the affected eye, though occasionally, you may also feel a minor irritation in your eye.
However, consult a doctor if you have a subconjunctival haemorrhage, your vision deteriorates, or you have red eyes.
The following are some possible causes of subconjunctival bleeding and red eyes:
- Excessively scratching your eyes
- Vomiting
- Sneezing or coughing
- Eye injury
You can be more susceptible to this illness if you take blood thinners and have diabetes or high blood pressure.
Eyelid stye can cause Red Eyes
A stye is an inflammation-causing obstruction of the meibomian gland in the eye. Your upper or lower eyelids, outer or inside, may be affected.
The edge of your eyelid may turn red, bloated, and painful if you have a stye. Due to the clogged gland, the affected area may fill with meibum and eventually develop to the size of a pea.
Angle-closure glaucoma can be a reason for Red Eyes
Glaucoma is when your eye pressure rises due to your eye producing more fluid than usual. Your optic nerve may be harmed, possibly resulting in blindness.
The condition of glaucoma comes in various forms. One kind, known as angle-closure glaucoma, causes an abrupt rise in ocular pressure. This kind of glaucoma may also go by the name closed-angle or narrow-angle.
Angle-closure glaucoma symptoms include the abrupt onset of red eyes. Other signs to watch out for include the following:
- Strong eye pain
- Seeing rainbow rings or halos and having blurry vision
- Reduced vision
- Headache
- Dizziness or vomiting
Angle-closure glaucoma develops when the iris covers the opening where ocular fluid exits the eye. Eye pressure quickly rises as a result of fluid beginning to accumulate in the eye. If you don't get treatment quickly for this type of glaucoma, you could lose your vision.
Corneal ulcers can cause Red eyes
Corneal ulcers are sores or ulcers that affect the cornea, the outside layer of the eye. A different name for this illness is keratitis.
Other signs of a corneal ulcer besides red eyes include:
- Intense eye pain
- Feeling that there is something in your eye,
- Increased crying
- Pus discharge
- Blurry vision
- Sensitivity to light
- Swelling of your eyelids
Numerous factors might lead to corneal ulcers:
- Dry eyes
- Sleeping in contact lenses
- Bacteria
- Viruses including herpes simplex and varicella-zoster viruses fungi Acanthamoeba- a type of parasite
- Using well water to clean contacts
- Swimming or showering with contact lenses or -scratching, cutting, or burning the cornea
- Diseases that interfere with the capacity of the eyelid to close, such as Bell's palsy
If you experience corneal ulcer symptoms, you must get medical help immediately. This illness might permanently harm your vision and lead to red eyes if it is not treated.
Contact lens wear can be a reason for Red eyes
Others who wear contact lenses have to touch their eyes and the region around them more frequently than people who don't. As a result, people are more likely to have eye redness or bloodshot eyes due to several circumstances. A few of these are:
- Corneal scrapes or scratches
- Allergies to eyes
- Eye diseases
- Corneal ulcers can develop if wearers sleep with their lenses on
- Dry eyes
- Neovascularization, which is the development of new blood vessels in the cornea
- Giant papillary conjunctivitis is a form of conjunctivitis that causes lumps to appear under your eyelid
- The inflammation-related syndrome is known as contact lens-induced acute red eye (CLARE), brought on by wearing contacts all night
Some signs of contact lens difficulties, in addition to red eyes, include:
- Eye discomfort
- Increasing tears
- Hazy vision
- Light sensitivity
Remove your contacts for a few hours if you wear contacts and experience any of the symptoms listed above. Call an eye doctor if your symptoms persist or get worse.
Additional causes of red eyes
In addition to the factors mentioned above, these other factors can also contribute to red eyes:
- Using drugs or alcohol can cause red eyes
- Photokeratitis - an eye irritation that can result from exposure to sunlight
- Ocular rosacea is a skin disorder that can affect your eyes, cheeks, nose, or forehead
- Trichiasis, in which the eye is irritated by the eyelashes growing inward
- Cellulitis - a skin inflammation caused by bacteria that can affect the eyelid or eye socket
- An infection of the tissues inside your eye, known as endophthalmitis
- Onchocerciasis, an illness brought on by a roundworm, can cause red eyes
- The cancer of the eye, called retinoblastoma